Types of Mosquitoes
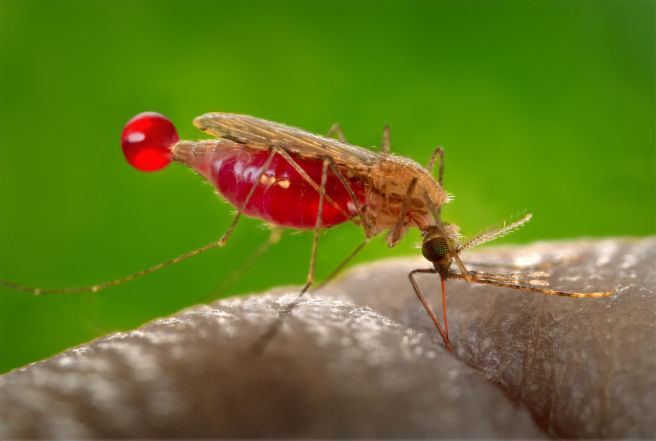

Anopheles Mosquito
Only the female Anopheles mosquito takes bloodmeals from humans, birds, mammals, and other vertebrates for egg development. Malaria is transmitted to humans by female mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles. Female mosquitoes take blood meals for egg production, and these blood meals are the link between the human and the mosquito hosts in the parasite life cycle.

Aedes Mosquitoes
These mosquitoes live in tropical, subtropical, and in some temperate climates. They are the main type of mosquito that spread Zika, dengue, chikungunya, and other viruses. Because Ae. aegypti mosquitoes live near and prefer to feed on people, they are more likely to spread these viruses than other types of mosquitoes.
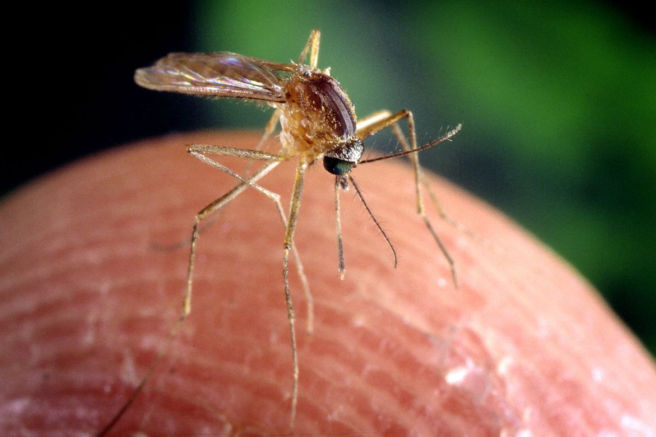
Culex Mosquito
One of the best-known summer pests, culex-mosquitoes breed in stagnant water or soft soil. Culex-Mosquitoes are vectors of numerous diseases including malaria, yellow fever, dengue fever, encephalitis and West Nile virus. Mosquitoes can breed in any form of stagnant water, including ponds, marshes, floodwaters, storm drains, old tires and water in tree holes.
